Devices pave way for the development of new treatments
Scientists have developed tiny, remote-controlled robots that release cancer-fighting compounds. It is hoped that the robots may someday be used to diagnose and treat illness in areas of the human body that are difficult to reach.
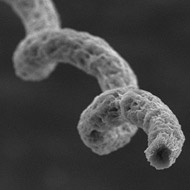
Developed by an international team of researchers, the ‘micro-robots’ are coated in microscopic algae with non-harmful, biocompatible magnetic particles. The devices are about the size of a blood cell and can swim in biological fluids, such as dilute blood and gastric fluid.
In experiments with rats, scientists used magnets to guide the robots to sites in the stomach. They could be tracked in tissue close to the surface of the skin by imaging the algae’s natural luminescence. In harder-to-reach tissue, they could be tracked using an MRI scanner.
Besides delivering drugs to areas of the body that are hard-to-reach, scientists say the robots could also sense chemical changes linked to the onset of illness. This could one day make them useful as probes for remote diagnosis.
The devices biodegrade within the body and can take more or less time depending on the thickness of their manufactured coating. Qi Zhou, of the University of Edinburgh’s School of Engineering, who worked on the study, said:
“A small-scale robot that can be remotely guided, is easily tracked and harmlessly biodegrades, potentially overcomes many of the challenges faced by minimally invasive therapies. We hope our discoveries will pave the way for the development of useful diagnostics or treatments.”
The study, published in Science Robotics, was carried out in collaboration with the Universities of Edinburgh and Manchester.
Image (C) Yan et al Science Robotics 2017.



 SPVS and FIVP have collaborated to launch a short survey about the proposed reform of the Veterinary Surgeons Act.
SPVS and FIVP have collaborated to launch a short survey about the proposed reform of the Veterinary Surgeons Act.