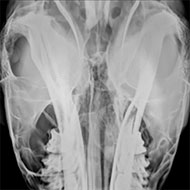
Cutting-edge imaging is improving the way veterinary surgeons diagnose and treat equine conditions of the head and spine, a new research collection suggests.
Efficient and accurate imaging of the intricate and less accessible parts of equine anatomy can be difficult due to the size and shape of the horse. Prior to the availability of CT and MRI over the past decade, radiographs were the only feasible option.
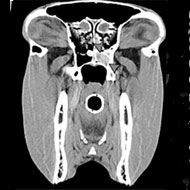
Now, with the development of larger, wider and more adaptable scanners, horses can be examined in a standing position, significantly improving diagnostic and treatment strategies as well as avoiding the need for general anaesthetic.
The Equine Veterinary Journal (EVJ) has teamed up with Equine Veterinary Education and Veterinary Radiology and Ultrasound to provide an online collection of the latest articles on head and spine imaging.
Three studies in the collection consider the benefits of MRI for the spine and neck, including the evaluation of 84 head disorders, diagnosing cervical stenotic myelopathy and assessing two foals with closed head trauma. A downside to MRI, however, is the size of scanners compared with the horse, which can make it a challenge to use. There is also a longer acquisition time than CT.
Advanced diagnostic techniques are also assisting with clinical and surgical approaches to problems with the equine head. Owing to its position, the sphenopalatine sinus is challenging to assess radiographically but CT can help to overcome this. One study looked at how CT can help to unravel the pathology of various equine sinonasal tumours.
CT is also useful for identifying defects in the bone and tooth, according to a study of horses with diseased mandibular cheek teeth, but is far less beneficial in identifying inflammation and tissue destruction - which is better served by MRI.
Despite these advances, one spinal evaluation article concludes that the horse's back still poses difficulties, primarily owing to its size. While new technologies - such as robotic fluoroscopy and cone-beam CT - could offer a cross-sectional method to evaluate the spine, radiographs are currently better for evaluating the findings of spinous process impingement seen on scintigraphy. The 'take home message' being that the wide variety of abnormalities seen on scintigraphy and radiography in horses with and without back pain means a diagnosis is more likely to be achieved by physical examination than imaging findings.
Anthony Pease, EVJ associate editor, commented: "Advanced imaging is still in its infancy with sequences still being developed to help optimise the time and detail needed for diagnosing complex musculoskeletal and neurologic disorders. Continued research in a controlled environment and comparing to histopathology will allow clinicians to further their knowledge and understanding of the CT and MRI findings in the equine patients."
Images supplied by Bright bay Consulting from the paper: ‘The role of the head computed tomography in equine practice’.



 The RCVS has announced a new version of its 1CPD mobile app, with enhanced features for veterinary surgeons and veterinary nurses to record their continuing professional development.
The RCVS has announced a new version of its 1CPD mobile app, with enhanced features for veterinary surgeons and veterinary nurses to record their continuing professional development.